LSP Tools: Bringing IDE Intelligence to Claude Code
If you’ve watched Claude Code grep through a large codebase looking for function references, you know the pain. Hundreds of matches scroll by—comments, string literals, similarly-named variables—and somewhere in that noise are the actual usages you care about.
It’s like using find when you need a map.
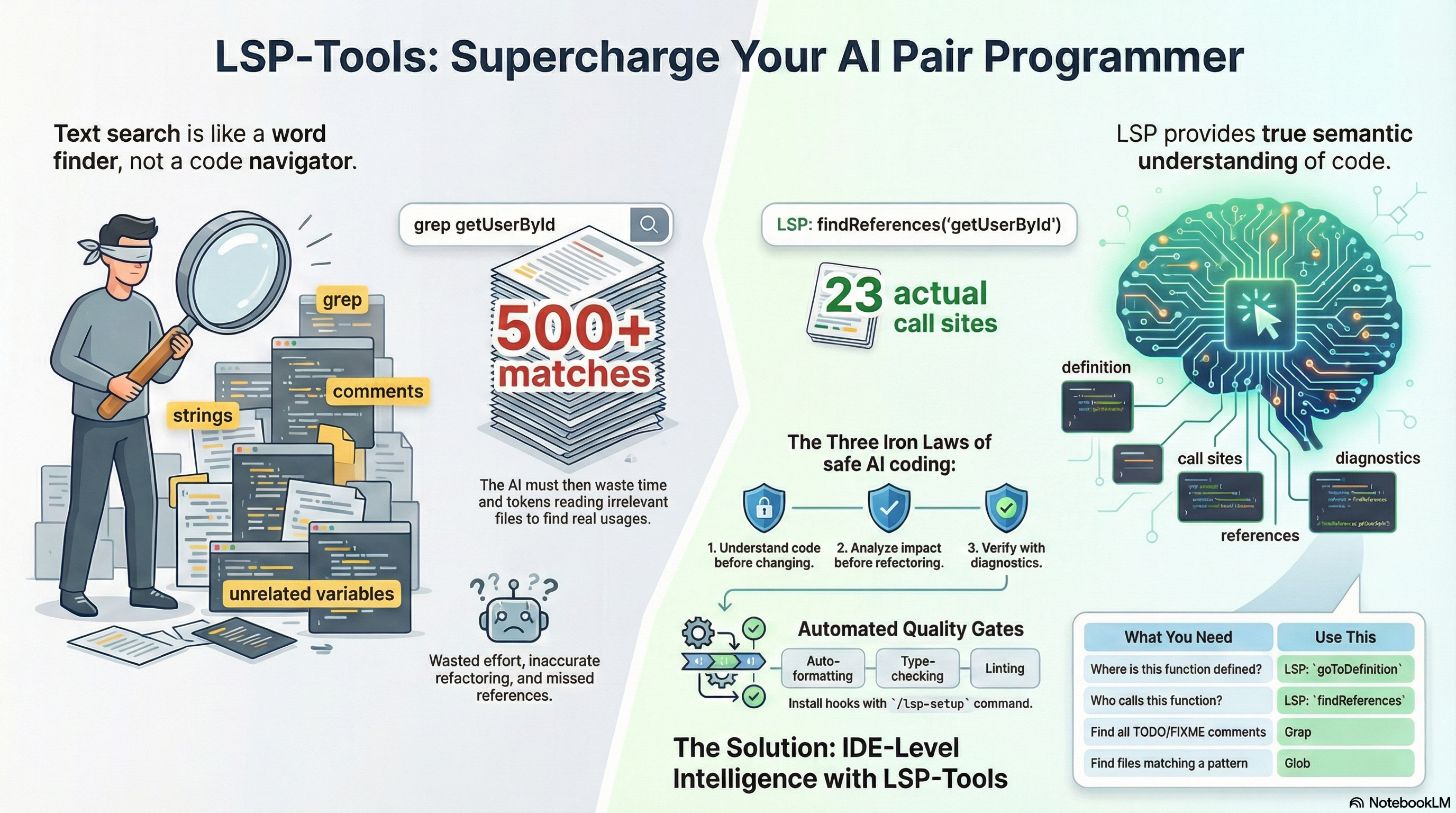
The Language Server Protocol has been available in Claude Code for a while now, but using it consistently requires discipline. The new lsp-tools plugin changes that equation: it enforces LSP-first code navigation with hooks, behavioral constraints, and per-language configuration that makes semantic code intelligence the default.
What LSP Brings to Claude Code
Language Server Protocol is the standardized interface that powers the “go to definition,” “find references,” and hover documentation features in modern IDEs. Instead of text matching, LSP provides semantic understanding:
| Operation | What It Does |
|---|---|
goToDefinition |
Jump to where a symbol is actually defined |
findReferences |
Find every usage of a symbol, not just text matches |
hover |
Get type signatures and documentation inline |
incomingCalls |
Trace who calls a function |
outgoingCalls |
Trace what a function calls |
The difference is substantial. A grep for getUserById in a moderately sized
project might return 500+ matches—comments, strings, similar function names,
type definitions. LSP findReferences returns the 23 actual call sites.
More importantly, LSP understands scope. A local variable named config in one
function is distinct from a module-level config elsewhere. Grep can’t know
that.
Why This Matters for AI-Assisted Development
Claude Code is remarkably capable, but it’s working with the same constraints as any developer: it needs to understand code before modifying it. The problem is that without LSP, understanding comes from reading large amounts of potentially irrelevant context.
Consider a refactoring task: “rename the processOrder function to
handleOrder.” Without LSP, Claude would need to:
- Grep for all occurrences of
processOrder - Read each file to determine if it’s a true reference
- Filter out false positives (comments, strings, other functions)
- Make changes and hope nothing was missed
With LSP, the workflow becomes:
findReferencesonprocessOrder—exact usages only- Make changes with confidence
The token savings are real. In a 100-file project, grep-based reference finding might consume 2000+ tokens scanning output. LSP returns exact matches in ~500 tokens.
The Three Iron Laws
The lsp-tools plugin doesn’t just enable LSP—it enforces patterns that prevent common mistakes. The skill defines three mandatory constraints:
1. NO MODIFYING UNFAMILIAR CODE WITHOUT goToDefinition FIRST
2. NO REFACTORING WITHOUT findReferences IMPACT ANALYSIS FIRST
3. NO CLAIMING CODE WORKS WITHOUT LSP DIAGNOSTICS VERIFICATION
These aren’t suggestions. The plugin activates when it detects trigger phrases like “find definition,” “before I refactor,” or “what calls this function,” and the behavioral patterns become part of Claude’s approach.
The pre-edit protocol requires understanding before modification:
- NAVIGATE:
goToDefinitionto understand implementation - ANALYZE:
findReferencesto assess change impact - INSPECT:
hoverto verify type signatures - THEN: Make changes
This mirrors what experienced developers do naturally—and prevents the “quick refactor” that misses half the call sites.
What the Plugin Provides
The lsp-tools plugin includes:
A core skill (lsp-enable) that defines behavioral enforcement patterns,
decision trees for choosing between LSP/Grep/Glob, and pre-edit/post-edit
protocols.
The /lsp-setup command that auto-detects languages in your project and
installs appropriate hooks:
# Auto-detect languages
/lsp-tools:lsp-setup
# Explicit language selection
/lsp-tools:lsp-setup typescript python go
Pre-configured hooks for 12 languages:
- TypeScript/JavaScript (vtsls)
- Python (pyright)
- Go (gopls)
- Rust (rust-analyzer)
- Java (jdtls)
- Kotlin (kotlin-language-server)
- C/C++ (clangd)
- C# (OmniSharp)
- PHP (phpactor)
- Ruby (ruby-lsp)
- HTML/CSS (vscode-langservers)
- LaTeX (texlab)
CLAUDE.md sections for each language with navigation patterns, quality gates, and language-specific tooling guidance.
Hooks Integration: Real-Time Quality Gates
Beyond LSP navigation, the hooks provide automated quality checks during
development. When you run /lsp-setup, it copies language-appropriate hooks
to your project’s .claude/hooks.json.
For TypeScript projects, you get:
{
"hooks": [
{
"name": "format-on-edit",
"event": "PostToolUse",
"matcher": "Write|Edit",
"command": "npx prettier --write $CLAUDE_FILE_PATHS"
},
{
"name": "typecheck-on-edit",
"event": "PostToolUse",
"matcher": "Write|Edit",
"command": "npx tsc --noEmit"
},
{
"name": "pre-commit-quality-gate",
"event": "PreToolUse",
"matcher": "Bash",
"command": "if echo \"$CLAUDE_TOOL_INPUT\" | grep -qE 'git commit'; then npx tsc --noEmit && npx eslint .; fi",
"blocking": true
}
]
}
Every file edit triggers formatting and type checking. Commits are blocked if the codebase has type errors or lint failures. Problems are caught when they’re introduced, not discovered later.
Python projects get equivalent hooks for ruff, pyright, and pytest. Go projects get gofmt, vet, and golangci-lint. Each language gets appropriate tooling without manual configuration.
Setup Instructions
Step 1: Enable LSP in Claude Code
You have two options for enabling LSP support:
Option A: Environment Variable
Add to your shell profile (~/.bashrc, ~/.zshrc, or
~/.config/fish/config.fish):
export ENABLE_LSP_TOOL=1
Reload your shell configuration:
source ~/.bashrc # or ~/.zshrc
Option B: Settings File (Recommended)
Configure LSP in your Claude Code settings files. This persists the setting without relying on shell environment.
For global configuration, add to ~/.claude/settings.json (or
settings.local.json for machine-specific settings):
{
"env": {
"ENABLE_LSP_TOOL": "1"
}
}
For project-specific configuration, add to <project>/.claude/settings.json:
{
"env": {
"ENABLE_LSP_TOOL": "1"
}
}
The settings file approach is cleaner for teams—commit the project-level
settings and everyone gets LSP automatically. You can also use
~/.claude/settings.*.json patterns for environment-specific configurations
(e.g., settings.work.json, settings.personal.json).
Step 2: Install Language Servers
Install the language servers for your languages:
# TypeScript/JavaScript
npm install -g @vtsls/language-server typescript
# Python
npm install -g pyright
# Go
go install golang.org/x/tools/gopls@latest
# Rust
rustup component add rust-analyzer
Step 3: Install the Plugin
# Add the marketplace if you haven't already
claude /plugin marketplace add https://github.com/zircote/marketplace
# Install lsp-tools
claude /plugin install lsp-tools
Step 4: Run Setup in Your Project
cd /path/to/your/project
/lsp-tools:lsp-setup
The command detects your project’s languages, installs appropriate hooks, and optionally adds LSP guidance to your CLAUDE.md.
Step 5: Restart Claude Code
LSP requires a fresh session to initialize properly. Restart Claude Code after completing setup.
Important: Version Compatibility
There’s currently a bug in the latest Claude Code release that affects LSP initialization. Until it’s resolved, I recommend using v2.0.67:
npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code@2.0.67
This version has stable LSP support without the race condition that can cause intermittent failures in newer releases.
The Decision Matrix
One of the plugin’s most useful features is clear guidance on when to use LSP versus other tools:
| What You Need | Use This |
|---|---|
| Where is this function defined? | LSP: goToDefinition |
| Who calls this function? | LSP: findReferences |
| What type does this return? | LSP: hover |
| Find TODO/FIXME comments | Grep |
| Search for configuration values | Grep |
| Find files matching a pattern | Glob |
LSP is for semantic operations—understanding code structure, types, and relationships. Grep remains appropriate for literal text searches. The plugin helps Claude choose correctly.
Why You Should Adopt This
If you’re using Claude Code for real development work, LSP support transforms the experience from “helpful assistant that sometimes misses things” to “pair programmer with IDE-level understanding.”
The benefits compound:
- Fewer false positives in reference searches
- More accurate refactoring that doesn’t miss call sites
- Better context understanding with less token consumption
- Faster navigation in large codebases
- Automatic quality gates that catch problems early
The plugin makes LSP the default rather than an option you have to remember.
Claude develops habits—use goToDefinition before modifying, check
findReferences before renaming, verify diagnostics before claiming success.
It’s a small change in tooling that produces a meaningful change in reliability.
LSP-Aware Agents in the Zircote Plugin
If you’re using the zircote plugin, you’ll find that 25+ specialist agents are already LSP-aware. When LSP is enabled, these agents automatically leverage semantic code navigation:
Language Specialists (02-language-specialists/):
typescript-pro,python-pro,golang-pro,rust-engineerjava-architect,kotlin-specialist,swift-expertreact-specialist,vue-expert,angular-architect,nextjs-developercsharp-developer,cpp-pro,php-pro,rubyspecialists
Quality & Security (04-quality-security/):
code-reviewer,debugger,refactoring-specialist
Developer Experience (06-developer-experience/):
documentation-engineer,build-engineer
These agents have LSP listed in their tools declaration, meaning they’ll use
goToDefinition, findReferences, and hover operations when navigating code.
The combination of lsp-tools behavioral enforcement and LSP-aware agents creates
a powerful feedback loop: agents understand code semantically, and the plugin
ensures they follow best practices.
To take advantage of this, install both plugins:
claude /plugin install lsp-tools
claude /plugin install zircote
Then enable LSP and watch agents like typescript-pro or python-pro navigate
your codebase with IDE-level precision.
The lsp-tools plugin is available from the zircote marketplace. For detailed setup instructions and troubleshooting, see the comprehensive LSP guide. LSP support was introduced in the Claude Code 1.0.3 release.
Comments will be available once Giscus is configured.